What Is CBD?
Cannabidiol—CBD—is a cannabis compound that has significant medical benefits, but does not make people feel “stoned” and can actually counteract the psychoactivity of THC. The fact that CBD-rich cannabis is non-psychoactive or less psychoactive than THC-dominant strains makes it an appealing option for patients looking for relief from inflammation, pain, anxiety, psychosis, seizures, spasms, and other conditions without disconcerting feelings of lethargy or dysphoria.
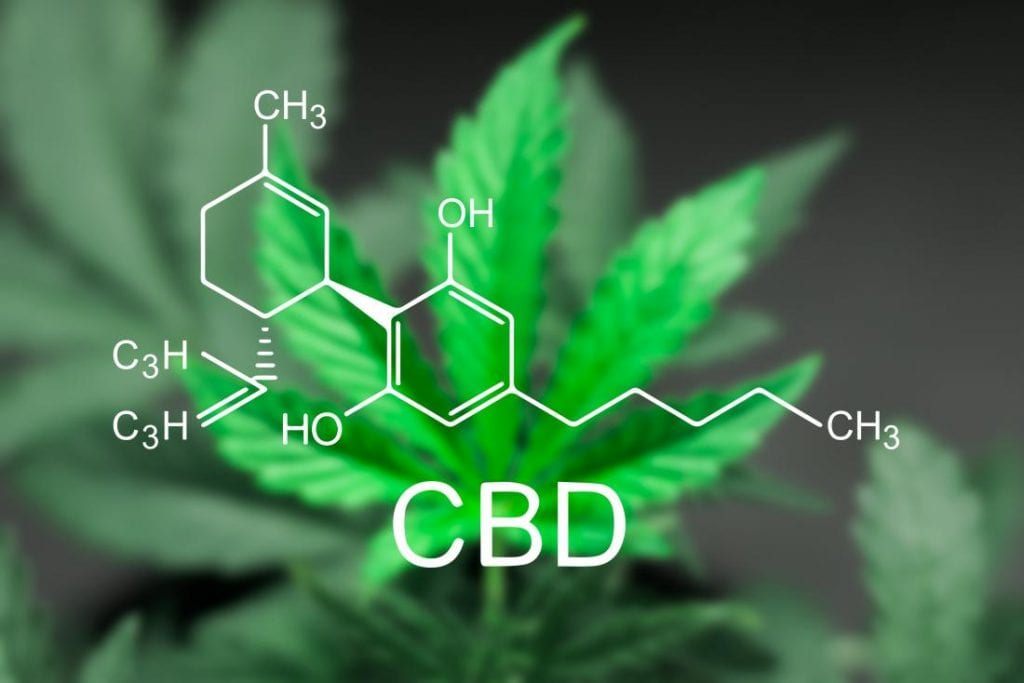
That’s right, without the high!
Scientific and clinical research—much of it sponsored by the US government—underscores CBD’s potential as a treatment for a wide range of conditions, including arthritis, diabetes, alcoholism, MS, chronic pain, schizophrenia, PTSD, depression, antibiotic-resistant infections, epilepsy, and other neurological disorders. CBD has demonstrable neuroprotective and neurogenic effects, and its anti-cancer properties are currently being investigated at several academic research centers in the United States and elsewhere. Further evidence suggests that CBD is safe even at high doses.
Project CBD responds to inquiries from all over the world. Almost everyone wants to know where to get CBD-rich products and how to use them for maximum benefit. After decades in which only high-THCcannabis was available in North America and beyond, CBD-rich strains and products are now available to medical users.
“CBD-rich” versus “CBD dominant:” By “CBD-rich,” we mean a cannabis strain or product that has equal amounts of CBD and THC, or more CBD than THC (usually at least 4 percent CBD by dry weight.). By “CBD-dominant,” we mean strains or products that are CBD-rich but have very little THC content
THE ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM
Cannabis has been at the center of one of the most exciting—and underreported—developments in modern science. Research on marijuana’s effects led directly to the discovery of a hitherto unknown biochemical communication system in the human body, the Endocannabinoid System, which plays a crucial role in regulating our physiology, mood, and everyday experience.
The discovery of receptors in the brain that respond pharmacologically to cannabis—and the subsequent identification of endogenous cannabinoid compounds in our own bodies that bind to these receptors—has significantly advanced our understanding of human biology, health, and disease.
It is an established scientific fact that cannabinoids and other components of cannabis can modulate many physiological systems in the human brain and body. Cannabinoids are chemical compounds that trigger cannabinoid (and other) receptors. More than 100 cannabinoids have been identified in the marijuana plant. Of these marijuana molecules, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) have been studied most extensively. In addition to cannabinoids produced by the plant, there are endogenous cannabinoids (such as anandamide and 2AG) that occur naturally in the mammalian brain and body, as well as synthetic cannabinoids created by pharmaceutical researchers.
Extensive preclinical research—much of it sponsored by the U.S. government—indicates that CBD has potent anti-tumoral, antioxidant, anti-spasmodic, anti-psychotic, anti-convulsive, and neuroprotective properties. CBD directly activates serotonin receptors, causing an anti-anxiety effect, as well.“Cannabidiol offers hope of a non-toxic therapy that could treat aggressive forms of cancer without any of the painful side effects of chemotherapy,” says McAllister.
In recent years, scientists associated with the International Cannabinoid Research Society (ICRS) have elucidated a number of molecular pathways through which CBDexerts a therapeutic impact. For example, a preclinical study by Dr. Sean McAllister and his colleagues at the California Pacific Medical Center in San Francisco report on how CBD destroys breast cancer cells by down-regulating a gene called ID-1, which is implicated in several types of aggressive cancer. Silencing the ID-1 gene is, thus, is a potential strategy for cancer treatment.
“Cannabidiol offers hope of a non-toxic therapy that could treat aggressive forms of cancer without any of the painful side effects of chemotherapy,” says McAllister.

The images above are from an experiment by McAllister testing how CBD can stop the invasion of cancer cells in human cell lines. Compare the untreated breast cancer cells on the left to the breast cancer cells destroyed by CBD on the right. Photo credit: The California Pacific Medical Center
CBD and THC Synergy
According to McAllister’s lab, the best results were obtained when CBD was administered along with THC. Several studies underscore the therapeutic advantages for combining CBD and THC—particularly for treating peripheral neuropathy, a painful condition associated with cancer, multiple sclerosis (MS), diabetes, arthritis, and other neurodegenerative ailments. Clinical research conducted by with GWPharmaceuticals, a British company, has also shown that CBD is most effective as an analgesic when administered in combination with whole plant THC
CBD oil has been the star of 2018, at least when it comes to health (and beauty, for that matter). And the pandemonium is warranted. The natural, holistic remedy has real medicinal use spanning from stopping seizures to alleviating anxiety and helping insomniacs get some much-needed rest—with little to no side effects, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
But CBD (an acronym for cannabidiol) oil isn’t a cure-all, despite what the best efforts of marketers the world over may tell you. “It doesn’t work for everything,” said Perry Solomon, M.D., a board-certified anesthesiologist and founder/chief medical officer of HelloMD. For example, “if you have a lung infection like bronchitis, you can’t put a cream on your chest—you need to take a Z-pack. You’re not going to cure something like that with cannabis.”
Those who are new to cannabis find CBD to be a great first step, because unlike psychoactive THC, CBD doesn’t give you the intoxication or “high” effect. It can be vaporized using a pen, but many patients using CBD as medicine are turning to sublingual tinctures, ingestible oils and treats, capsules, and even topical products.
There are a lot of claims out there about what CBD supposedly cures—and it’s still early on in the research game for cannabidiol. The good news? “CBD doesn’t cause any harm,” said Dr. Solomon (and WHO agrees). “The placebo effect is very strong, but it’s not harmful.”
It’s still early days of CBD research (particularly in the U.S.); government regulations have prohibited much scientific research and funding when it comes to CBD as medicine in the past few decades. However, what has been researched and proven is pretty incredible—and thanks to changing laws, more is coming.
Here, we break down what we know about the benefits of CBD oil and what it can treat so far, including what’s been studied, what doctors are saying, and what’s still left up to interpretation.
Epilepsy and Seizures
This year, the FDA approved a CBD-based drug to treat seizures, which was a huge step in making this natural medicine more available to the public and to patients who need it to survive. To date, of all the reported health benefits of CBD oil, this has been the most researched (and proven) use.
Anxiety and Mood Disorders
CBD has been touted as a bona fide anxiolytic, and possibly an antidepressant. Whether it’s social anxiety or generalized anxiety disorder, CBD may be the solution you’re looking for. “Most patients seem to be using CBD as an anxiolytic [anti-anxiety medication]… it helps calm them down and relax them,” said Dr. Solomon. “The biggest clinical studies [that have been done] show it does help decrease anxiety when you take 300 to 600mg of CBD.”
If you’re considering using CBD Oil or Delta 8 THC as a medication for your anxiety or mood disorders, first consult with your psychiatrist and/or physician.
Psychosis
In addition to mood disorders, CBD is also known to help patients with psychosis—some doctors have called it a legitimate antipsychotic, and a study from just this year called CBD “a new class of treatment for the disorder.”
Recent research, including animal studies, have suggested that “CBD has a pharmacological profile similar to that of atypical antipsychotic drugs,” and additionally have encouraged more research to evaluate its ability to treat similar illnesses and disorders, like bipolar disorder.
Migraines
Cannabidiol oil may relieve pain and reduce inflammation, and it shows some promise as a treatment for migraines.
Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of more than 120 substances in cannabis.
CBD comes from the cannabis plant, and it is a different compound than tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which produces a high. CBD has no mind-altering effects.
As migraine sufferers continue to search for relief that won’t overload their bodies with pharmaceuticals, science continues to rise to the challenge. CBD oil is one of many tools migraineurs can use to try to reduce their pain and their reliance on pharmaceuticals, with the associated side effects. With its track record of safety and non-addictive nature, CBD oil could be worth a try for many migraine sufferers.
Insomnia
Have you heard about CBD oil for sleep issues? If you’re looking to catch up on some zzz’s, or you’re fighting a legitimate bout of insomnia, CBD may be able to help you fall—and stay—asleep. Some smaller studies have shown that CBD at bedtime could improve sleep, and a study on rats in 2013 showed that CBD increased total sleep time. That said, Jordan Tishler, M.D., noted that the rat study found “at high doses, CBD can cause insomnia and jitteriness”—so do your research on the appropriate dosage for each product before you go overboard. (Related: Can CBD Products Help You Sleep Better?)
Inflammation
Aside from being an antiseizure and antianxiety remedy, CBD is also known as an anti-inflammatory. Delivery for internal and muscular inflammation is recommended to be taken orally (sublingually, ingested, or vaporized) versus topically, which hasn’t been backed by clinical studies. Topical application can also be a viable option of applications for certain patients and conditions. (See: Do CBD Pain-Relief Creams Really Work?)
Pain
CBD could potentially be as effective for pain relief as an opioid, but without the potential for deadly addiction. Dr. Solomon shared a self-report study he conducted at UC Berkeley last year, which tracked patients that were using opioids for pain relief. When subjects tried using cannabis in lieu of opioids, the majority “reported that cannabis provided relief on par with their other medications, but without the unwanted side effects.” He noted that more research needs to be done, but all signs point to pain relief—which would lead to fewer opioid-related deaths.
Additionally, animal studies have been conducted to find that CBD may be a potential treatment for arthritis, and one report concluded that “there is substantial evidence that cannabis is an effective treatment for chronic pain in adults.” Dr. Tishler, however, credited THC as the pain-reliever in this case, not CBD.
Skin Ailments
As it is an anti-inflammatory, you may find CBD skin-care productshelpful when applied topically. Some research even points to its efficacy as an acne treatment, since it may limit inflammation in the sebum-producing glands that can lead to breakouts. If you’re not having luck with traditional acne-fighting ingredients (like salicylic acid), it may be worth giving it a shot.
As for anti-aging beauty products (yes, there are anti-aging CBD products) such as serums, creams, cleansers—you name it—the jury’s out. Unfortunately, searches through medical archives yielded nothing substantial, but it can’t hurt to try (well, only your wallet). As always, consult with your dermatologist first.
Crohn’s and IBD
Because studies are pointing to cannabinoids as a promising treatment for inflammation, CBD may, in fact, be a treatment for inflammatory bowel disease, including Crohn’s. While there is some initial evidence, there’s not a ton of clinical backing just yet. Stay tuned.
Degenerative Diseases
WHO’s 2018 report showed that CBD may be a therapeutic treatment for Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, and multiple sclerosis. Many reports say that, though results look good in small studies, more clinical research is needed to know for sure.
Cancer Treatment
There is mounting evidence that CBD could potentially fight cancer and, at the very least, help ease symptoms of cancer and side effects of chemotherapy. A 2006 studypublished in the Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics found, for the first time, that CBD potently and selectively inhibited the growth of different breast tumor cell lines.
And while there are some studies being done to see if CBD is anti-tumor, it is not recommended to use CBD in lieu of chemotherapy. “I would never recommend someone stop seeing an oncologist or stop medication their oncologist recommended to take CBD,” said Dr. Solomon. “I would add it as an adjunct to that medication, letting the oncologist know that they’re taking it.” The stories you may hear by word of mouth claiming that CBD alone cured someone’s cancer? Purely anecdotal as of now.
Heart Health
More research needs to be done, but there is some evidence CBD can protect the heart against vascular damage caused by high glucose, inflammation, or type 2 diabetes, according to a 2013 study published in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. The European Journal of Pharmacology also published a study earlier this year that pointed toward CBD aiding heart health. Perhaps what is most interesting is that CBD could mitigate the negative cardiovascular effects of stress and high blood pressure, providing a potential alternative to traditional medications used to lower blood pressure.
